Gross Retention vs. Net Retention: Definitions, Formulas, Examples

As both gross retention and net retention are crucial metrics in evaluating revenue dynamics in SaaS, it is best to perceive them as complementary rather than opposing metrics. By understanding the fundamentals of your company’s customer retention (GRR) and being able to identify the opportunities for upsells and cross-sells (NRR), you are getting a full overview of your company’s revenue streams and potential.
In the further exploration of net retention and gross retention, we’ll thoroughly explain their definitions, share the given formulas, and provide straightforward examples. Ready to learn how to get an extensive view of how your business is retaining and growing its customer base?
Let’s go.
What is Gross Revenue Retention (GRR)?
The gross retention rate measures the percentage of revenue retained from existing customers without taking expansions and any other additional sales into account. The gross revenue retention rate shows (solely) the company’s ability to maintain its current customers’ revenue over a certain period.
How to Calculate Gross Revenue Retention (GRR)?
To calculate the GRR formula, you’ll again need to get familiar with the revenue from existing customers at the end and start of the given period. The revenue at the end includes all the revenue gained from existing customers, regardless of the initial source, and the one at the start of the period is related to the initial revenue gained from the existing customers. Here’s the gross revenue retention formula:

Now, to differentiate between net retention and gross retention, let’s learn more about rate interpretation. If the GRR rate is above 100%, that means that the company has retained and potentially expanded its revenue from existing customers. With a rate of 100%, the company was able to retain its existing customer revenue without any gains or losses, and in the case where the rate is under 100%, there was a reduction in revenue due to downgrades or churn.
Gross Revenue Retention Rate: Example
Now, the difference between GRR and NRR can be seen through a simple example. Let’s say that the company had revenue of $600,000 at the start of the period and $550,000 at the end. The GRR rate is 91.6% in this case. Let’s explain how.
GRR = revenue at the end ($550,000) /revenue at the start ($600,000) x 100 = 91.6%.
This calculation proves that the company had churn or downgrades, as the result is below 100%. This reduction in revenue can only be attributed to these two factors, as the GRR rate only considers the retention aspect without taking additional sales or expansions into account.
What is Net Revenue Retention (NRR)?
Net Revenue Retention (NRR) stands for the summary of retained, expanded, and contracted revenue over a certain period. It calculates total revenue, including expansion, minus revenue churn.
The net revenue retention rate shows the company’s ability to retain and grow its revenue from existing customers, accounting for all upsells, cross-sells, expansion, and contraction (churn, downgrades).
How to Calculate Net Revenue Retention (NRR)?
Net revenue retention or “net dollar retention,” is extremely important in the SaaS industry as it measures both retention and the company’s ability to keep customers engaged and motivated, and whether its product is constantly updated and ready to meet the needs of different customer segments. Here’s the net revenue retention formula:
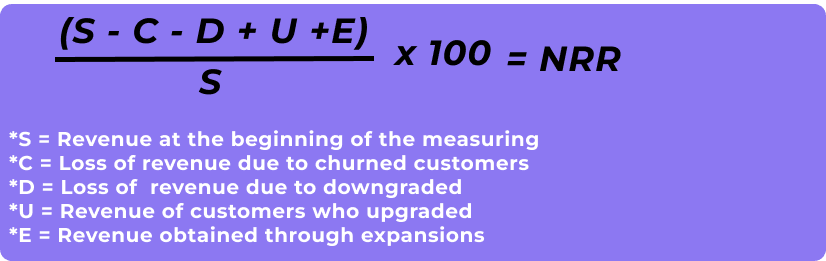
To fully understand net retention vs. gross retention differences, we first need to know how to interpret both NRR and GRR. If the Net Revenue Retention Rate is above 100%, the company is experiencing net revenue growth from its existing customers. If the NRR is 100%, the revenue flow is stable. For example, the revenue gained from upsells and expansions equals the lost revenue from a downgrade or churn. Finally, if the NRR is below 100%, it indicates a net revenue contraction, i.e., the revenue generated from upsells or expansions didn’t exceed the contraction.
Net Revenue Retention Rate Example
To clarify gross vs. net retention differences, we’ll share with you a simple example. Let’s say a company had revenue of $1.000,000 at the start of the given period (S), including expansion revenue of $50,000 and contraction revenue of $30,000. Now, at the end of the quarter, the revenue was $1.020,000, with a net change in revenue (E) of $20,000. In this case, the net retention rate is 2% – we simply divide S by E and multiply it by 100 to get the percentage.
Gross Retention vs. Net Retention: Which Is More Important to Track?
Companies use gross retention to show them how much revenue they are able to maintain from their current customers without the activities that increase customer value. On the other hand, net retention shows how much revenue you’re gaining when the given revenue-increasing factors are included in the equation. Therefore, you’ll need to track and calculate both metrics to get a bigger picture and understand the efficiency of implemented retention strategies
Both NRR and GRR are crucial metrics to track if you want to evaluate the overall health of SaaS businesses but also gain insights into the dynamics of customer revenue. Still, its importance differs based on the company’s goals, structure, size, and many other factors.
For example, for a SaaS startup, it might be more critical to track gross retention to understand the fundamentals of customer retention without the complexity of expansions. This is the best way to evaluate initial revenue stability.
As the company grows, NRR becomes more important as it provides insights into the company’s ability to expand revenue and drive growth. When creating and implementing customer success strategies where the goal is to maximize revenue from each customer, it is important to track NRR as well. Also, investors would like to get familiar with your NRR rates to evaluate your ability to retain customers and use expansion opportunities.
Therefore, we can conclude that tracking both metrics is important to stay updated about your company’s overall health and performance. In the beginning, you may require fundamental knowledge about your revenue streams and dynamics that comes with GRR assessment, while the situation changes once the company starts to grow and requires a more holistic view that comes with NRR.
Gross Retention vs. Net Retention — Conclusion
Gross retention and net retention are two critical metrics in SaaS, where each offers different insights into a company’s revenue oscillations. Gross retention serves as a fundamental metric to evaluate customer retention efforts, while Net Retention provides a full overview of the company’s ability to not only retain customers but also apply effective strategies to get additional revenue from the existing customer base.
Therefore, the given metrics should complement each other to help you get the most nuanced understanding of revenue changes. You can identify areas for improvement more easily when the metrics are not satisfactory and work on creating efficient retention strategies that will align with your customer base’s requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is Gross Retention important for SaaS companies?
GRR provides a basic understanding of a SaaS company’s ability to maintain revenue stability from existing customers without depending on upsells, cross-sells, and upgrades. This is how the core retention efforts of the company are assessed.
When should tracking GRR become a priority for a SaaS company?
A company in its earliest stages or one that is primarily interested in understanding and optimizing customer retention efforts, should prioritize tracking GRR. It provides a basic measure before any additional revenue streams are considered.
Can a company track both metrics simultaneously?
Yes, this is the usual case. The given metrics provide complementary insights, and tracking both allows you to gain a comprehensive evaluation of your company’s performance and revenue oscillations.
How do these metrics contribute to strategic decision-making?
This is a great question! By providing insights into the effectiveness of your customer retention campaigns and overall recurring revenue growth potential, the given metrics can serve as a guide in optimizing strategies for expansion, stability, and long-term success.